Obtaining inpudata
Rmarkdown 1: Downloading data.
Downloading datasets using curatedMetagenomicData, which contains the HUMANN or Metaphlan results.
Loading packages
knitr::opts_chunk$set(warning = FALSE)
library(dplyr)
library(tibble)
library(curatedMetagenomicData)
#library(curatedMetagenomicAnalyses)
# rm(list = ls())
options(stringsAsFactors = F)
options(future.globals.maxSize = 1000 * 1024^2)
Investigating potential response variables
- These are the 10 study conditions most commonly found in curatedMetagenomicData:
data("sampleMetadata")
availablediseases <- pull(sampleMetadata, study_condition) %>%
table() %>%
sort(decreasing = TRUE)
availablediseases
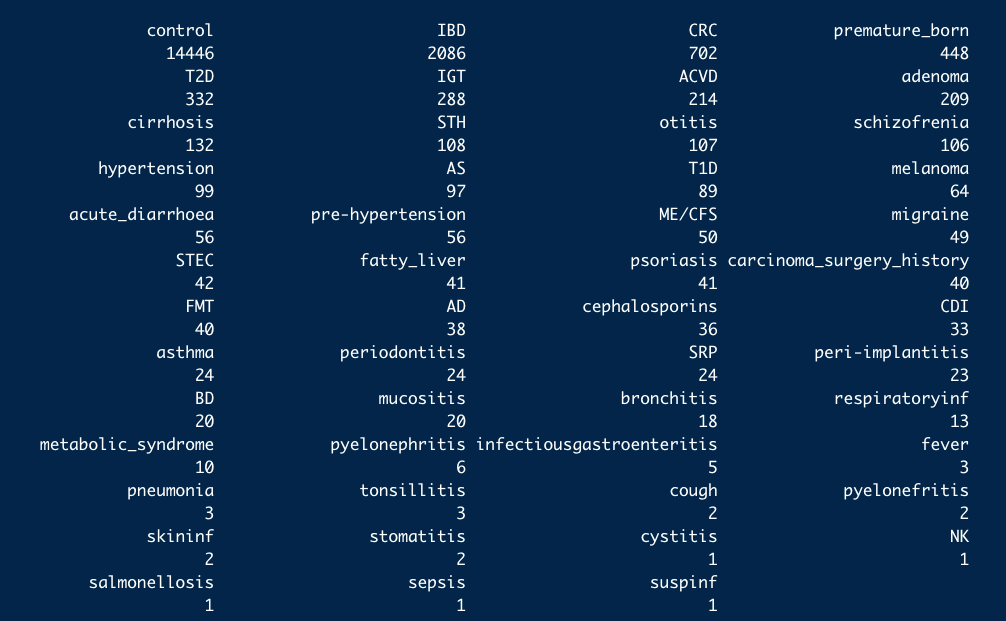
- And the number of studies they are found in:
studies <- lapply(names(availablediseases), function(x){
filter(sampleMetadata, study_condition %in% x) %>%
pull(study_name) %>%
unique()
})
names(studies) <- names(availablediseases)
studies <- studies[-grep("control", names(studies))] #get rid of controls
studies <- studies[sapply(studies, length) > 1] #available in more than one study
studies

- Each of these datasets has six data types associated with it; for example:
curatedMetagenomicData(pattern = "YachidaS_2019.+",
dryrun = TRUE,
counts = TRUE,
rownames = "long")
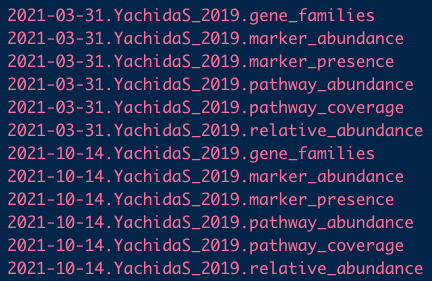
The metagenomics datasets contain more than 13 types data, which comprising taxonomic and functional profile with relative and absolute abundance matrix.
- Relative abundance: storing into TreeSummarizedExperiment object
YachidaS_2019_dataset <- curatedMetagenomicData(pattern = "YachidaS_2019.+relative_abundance",
dryrun = FALSE,
counts = TRUE,
rownames = "long")
YachidaS_2019_RB_TSE <- YachidaS_2019_dataset$`2021-10-14.YachidaS_2019.relative_abundance`
YachidaS_2019_RB_TSE
Write relative abundance datasets to disk
if (0) {
for (i in seq_along(studies)){
cond <- names(studies)[i]
se <-
curatedMetagenomicAnalyses::makeSEforCondition(cond, removestudies = "HMP_2019_ibdmdb", dataType = "relative_abundance")
print(paste("Next study condition:", cond, " /// Body site: ", unique(colData(se)$body_site)))
print(with(colData(se), table(study_name, study_condition)))
cat("\n \n")
save(se, file = paste0(cond, ".rda"))
flattext <- select(as.data.frame(colData(se)), c("study_name", "study_condition", "subject_id"))
rownames(flattext) <- colData(se)$sample_id
flattext <- cbind(flattext, data.frame(t(assay(se))))
write.csv(flattext, file = paste0(cond, ".csv"))
system(paste0("gzip ", cond, ".csv"))
}
}
Preparing for machine learning
metadata
relative abundance profile
metadata <- colData(YachidaS_2019_RB_TSE) %>%
data.frame()
phenotype <- metadata %>%
dplyr::select(disease) %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("SampleID") %>%
dplyr::filter(disease %in% c("CRC", "healthy"))
profile <- assay(YachidaS_2019_RB_TSE)
sid <- intersect(phenotype$SampleID, colnames(profile))
prof <- profile %>%
data.frame() %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("TaxaID") %>%
dplyr::group_by(TaxaID) %>%
dplyr::mutate(TaxaID_new = unlist(strsplit(TaxaID, "\\|"))[7]) %>%
dplyr::select(TaxaID, TaxaID_new, all_of(sid)) %>%
dplyr::ungroup() %>%
dplyr::select(-TaxaID) %>%
dplyr::rename(TaxaID = TaxaID_new)
phen <- phenotype %>%
dplyr::filter(SampleID %in% sid)
output
if (!dir.exists("./dataset")) {
dir.create("./dataset", recursive = TRUE)
}
write.csv(phen, "./dataset/metadata.csv", row.names = F)
write.table(prof, "./dataset/species.tsv", sep = "\t", quote = F, row.names = F)
Session info
devtools::session_info()